1. Overview
- Intervertebral discs act as shock absorbers and allow spinal mobility.
- Disc problems occur due to degeneration, herniation, or trauma.
2. Types of Disc Problems
- Disc degeneration
- Disc bulge
- Disc herniation (protrusion, extrusion, sequestration)
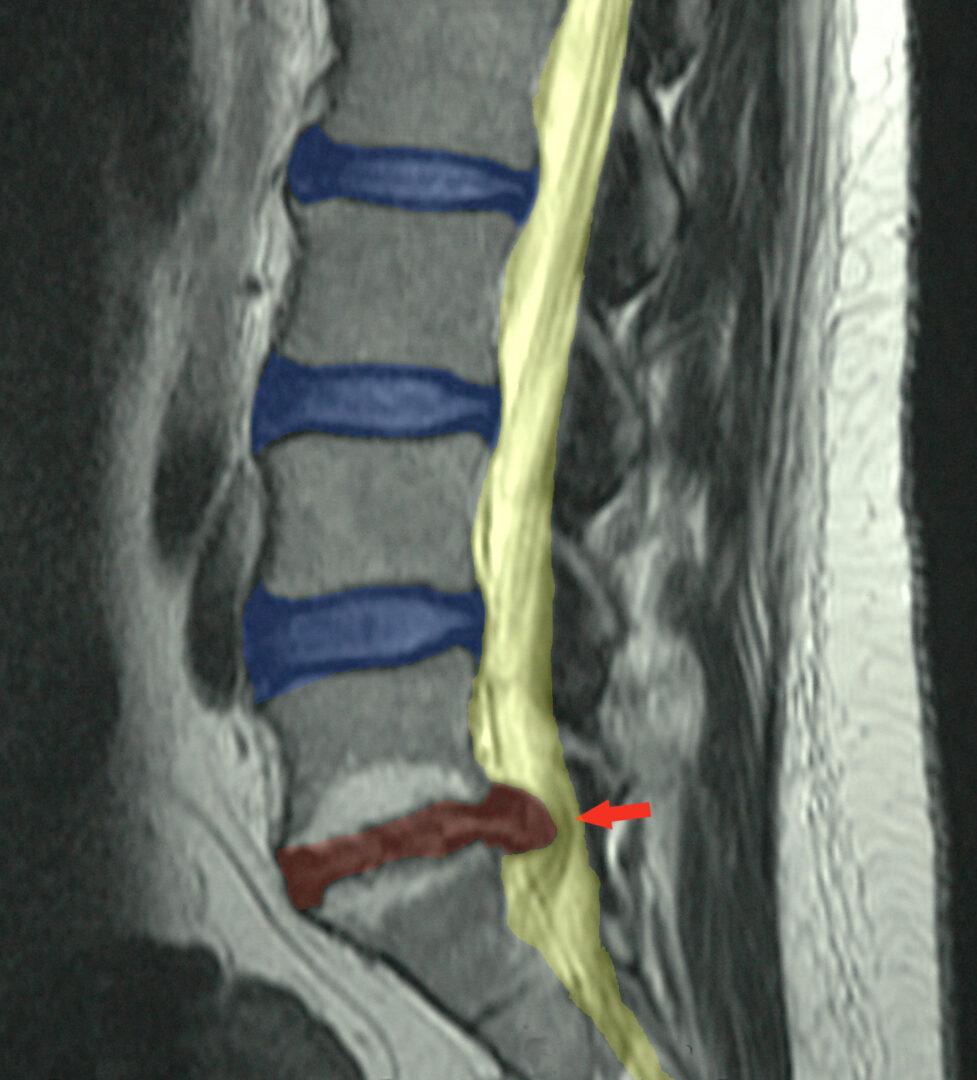
3. Causes
- Age-related wear and tear
- Repetitive stress and poor posture
- Trauma or heavy lifting
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle
4. Clinical Features
- Neck pain or low back pain
- Radiating pain to upper or lower limbs (radiculopathy)
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness
- In severe cases, spinal cord compression or myelopathy
5. Diagnosis
- Clinical examination
- X-rays for alignment and degeneration
- MRI for disc pathology and neural compression
6. Conservative Management
Most patients get well with conservative management and do not require any surgery.
- Rest and activity modification
- Analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications
- Physiotherapy and core-strengthening exercises
- Lifestyle and ergonomic modifications
7. Interventional Pain Procedures
Day care procedures.
- Epidural steroid injections
- Selective nerve root blocks
8. Surgical Management
- Indicated for neurological deficit or failure of conservative treatment
- Procedures include discectomy, microdiscectomy, endoscopic discectomy
- Fusion or disc replacement in selected cases
9. Outcome
- Most patients improve with conservative treatment
- Timely intervention leads to good pain relief and functional recovery